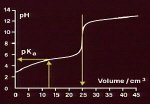
pKa
When a weak acid , denoted by HA, is put into water it dissociates into hydrogen ions and base ions A- according to the equilibrium
HA + H2O = H3O+ + A-
This equilibrium is governed by an equilibrium constant Ka . By analogy with pH, this equilibrium constant is defined by the relationship
pKa = - log10 Ka ([ HA ] / [ A- ])
For a strong acid which is highly dissociated the value of pKa is small whereas for a weak acid which is only partially dissiated the pKa is large.